The 60cm Reflector Telescope
|
About the 60cm reflector telescope
|
|
The 60cm reflector telescope was constructed in 1965. This telescope was
initially located at Kwasan observatory, but was transfered to Hida
observatory in 1968, shortly after its opening. Since
its construction, this telescope has been used for observations
which require a wide field of view, such as studies of comet's tails. More
recently, in order to study stellar atmospheres (especially of variable
stars), we have been improving the telescope's imaging devices and
spectrometers.
|
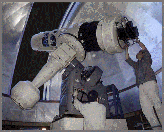
The 60cm telescope in the dome.
|
|
The performance.
|
|
| Apature | 600mm |
| Manufactured by | Tsugami Co. Ltd. |
| Focal length | 3300 mm (Newton focus: Main focus) |
| | 12000 mm (Cassegrain focus) |
| F/ratio | 5.5 (Newton focus) |
| | 20.0 (Cassegrain focus) |
| Resolution | 0"19 |
| Light gathering power | 7,400 |
| Limitting visual magnitude | 16.1 |
| Tracking accuracy | 1.5"/30' |
| Size of the housing | 860mm(diameter)x3,700mm |
| Total weight | 4.5 ton |
|
|
With and without the B/V/R/I filters by Johnson/Cousins(Bessel), we
usually perform intensity measurements of stars by cooling the CCD
camera with liquid nigtrogen. We are also developing a new spectrometer.
|
|
Recent topics
|
|
|
|
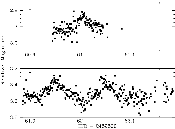
The left figure demonstrates an ultra intense brightening (up to
100 times the usual intensity) of the cataclysmic variable star "MN
Dra" in Dragon over a period of two weeks. A "cataclysmic star" is a kind of
"variable star", but changes its intensity more rapidly than most
variable stars.
The x-axis is the Julian Date, and the Y-axis is the relative
magnitude*1 against the reference star.
|
|
Such significant brightenings are considered to be caused by rapid
heating of the accretion disk*2. From this figure, one can
see a 25 % intensity-variation in a period of just 2.5 hours, and thus
infer that the accretion disk is distorted by the tidal forces caused
by the disk and companion's rotation.
|

A snap shot of "MN Dra" taken by the 60cm Refractor.
|
|
- The intensity of a variable star is obtained by measuring the
relative difference in intensity between the star and the nearby
non-variable star (reference star).
- A gasous object rotating in the form of a disk around a very heavy object (c.f.: right figure).
A model picture of an accretion disk. The gas of the companion star
(right) flows onto the left-hand object due to its significant gravity. An accretion disk is thus formed. (Copyright: Mark A. Garlick/space-art.co.uk)
|

|
|
Recent results.
|
|
| |
Photometric Observations of an SU UMa-type Dwarf Nova, VW Coronae
Borealis, during Outbursts
|
D. Nogami, M. Uemura, R. Ishioka, T. Kato, J. Pietz, 2004,
2004, PASJ, 56, S155
|
|
In-the-gap SU UMa-type dwarf nova, Var73 Dra with a supercycle of
about 60 days
|
D. Nogami, et al.,
2003, A&A, 404, 1067
|
|
Structure in the early afterglow light curve of the gamma-ray burst
of 29 March 2003
|
M. Uemura, et al.
2003, Nature, 423, 843
|
|

